When it comes to selecting energy-efficient windows for your home or building project, understanding U-values is crucial. The U-value is a measurement of how effective a window is at preventing heat transfer and plays a significant role in overall energy efficiency. This article will discuss the importance of window U-values, how they are calculated, and what to consider when choosing windows with optimal thermal performance.
What Are Window U-Values?
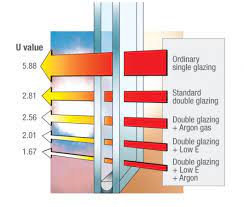
U-values, also known as thermal transmittance values, measure the rate of heat transfer through a window’s components, including the glass, frame, and spacer bars. A lower U-value indicates better insulation and less heat transfer, resulting in increased energy efficiency and reduced heating and cooling costs.
Factors Affecting Window U-Values
Several factors can influence a window’s U-value, including:
- Glazing type: Double-glazed windows typically have higher U-values than triple-glazed windows due to the additional layer of insulation provided by the third pane of glass.
- Low-E coatings: Low-emissivity coatings can significantly reduce a window’s U-value by reflecting heat back into the building.
- Gas fills: Argon or krypton gas fills between the glass panes can help lower the U-value by providing better insulation than air.
- Frame materials: Different frame materials, such as aluminum, wood, or uPVC, can impact the U-value due to their varying insulating properties.
How U-Values Are Calculated
Window U-values are calculated by measuring the rate of heat transfer through the various components of a window, including the glass, frame, and spacer bars. This is typically expressed in watts per square meter Kelvin (W/m²K). Lower U-values indicate better thermal performance, while higher U-values suggest less effective insulation.
Comparing U-Values and Energy Ratings
In addition to U-values, windows are often assigned energy performance ratings, such as the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) label or the European Union’s energy label. These ratings take into account multiple factors, including U-values, solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), and visible light transmittance. Comparing U-values alongside energy ratings can provide a more comprehensive understanding of a window’s overall energy efficiency.
Choosing Windows with Optimal U-Values
To maximize energy efficiency, select windows with low U-values that meet or exceed local building codes and energy performance requirements. Keep in mind that the optimal U-value may vary depending on factors such as climate, building orientation, and architectural design.